Fermentation is another anaerobic (non-oxygen-requiring) pathway for breaking down glucose, one that’s performed by many types of organisms and cells. In fermentation, the only energy extraction pathway is glycolysis, with one or two extra reactions tacked on at the end. Fermentation and cellular respiration begin the same way, with glycolysis.
Do You Have Low Energy? – Upgrade Your Power Supply # EVOO – Blog # 64 – The Virgin Olive Oiler
8 Chapter 8 Respiration Respiration by Yeast BACKGROUND. During respiration, yeast undergo metabolic processes to obtain energy from the breakdown of sugars. However, yeast can only metabolize certain types of sugars. In order for yeast to utilize a particular sugar as a food source, it needs to have specific transport mechanisms to bring the sugar molecules into its cells.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
The mitochondrial genome of R. americana contains 97 genes of which 92 can be assigned a function (Lang et al. 1997).The gene set comprises 18 protein-coding genes that have not been found in other mitochondrial genomes, but perhaps more interesting is the fact that it contains all of the 44 protein-coding genes previously identified in one or more other non-plant mitochondrial genomes

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Cellular Respiration | Definition, Steps & Importance – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Mitochondria perform numerous biological tasks ranging from bioenergetics to production of protein co-factors, including heme and iron-sulfur clusters. Due to the importance of mitochondria in many cellular processes, mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in a wide variety of human disorders.

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Yeast Have Mitochondria And Can Perform Cellular Respiration
Mitochondria perform numerous biological tasks ranging from bioenergetics to production of protein co-factors, including heme and iron-sulfur clusters. Due to the importance of mitochondria in many cellular processes, mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in a wide variety of human disorders. 1. Introduction Mitochondria of eukaryotic cells are surrounded by two biological membranes. The outer membrane that separates mitochondria from the cytosol is permeable for solutes due to the presence of voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC).
Cellular Respiration | Overview & Examples – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
Q3.1. Yeast have mitochondria and can perform cellular respiration. What would you expect to be consumed and produced during the process of cellular respiration in yeast? Glucose and O₂ consumed; CO2, H₂O, and energy produced. Glucose, H₂O, CO2, and energy consumed; O₂ produced. CO₂ and H₂O consumed; glucose, O₂, and energy produced. Cells | Free Full-Text | Mitophagy in Yeast: Decades of Research
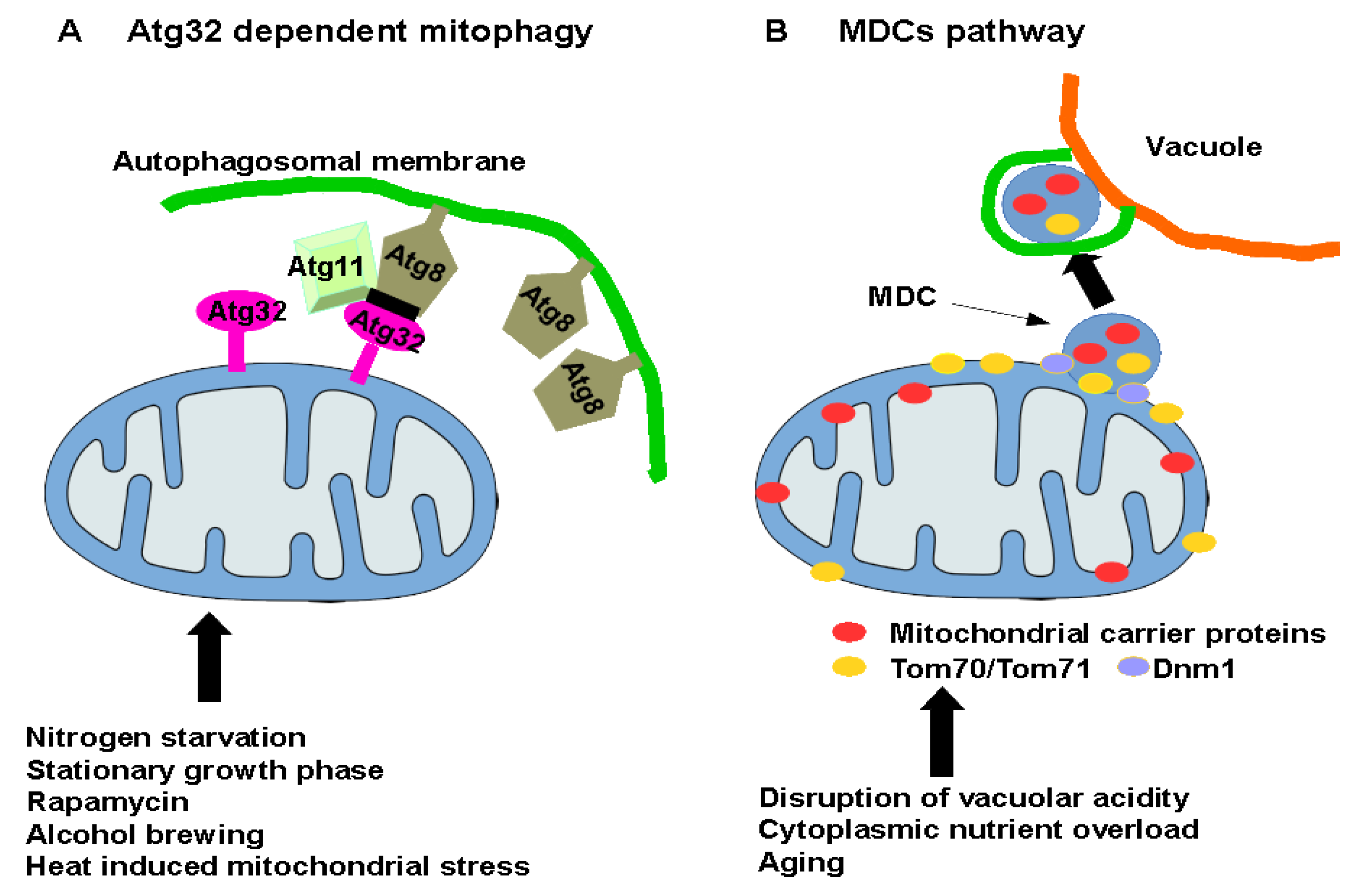
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Cells | Free Full-Text | The Role of Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitotic Fission in Regulating the Cell Cycle in Cancer and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Implications for Dynamin-Related Protein 1 and Mitofusin2 in Q3.1. Yeast have mitochondria and can perform cellular respiration. What would you expect to be consumed and produced during the process of cellular respiration in yeast? Glucose and O₂ consumed; CO2, H₂O, and energy produced. Glucose, H₂O, CO2, and energy consumed; O₂ produced. CO₂ and H₂O consumed; glucose, O₂, and energy produced.
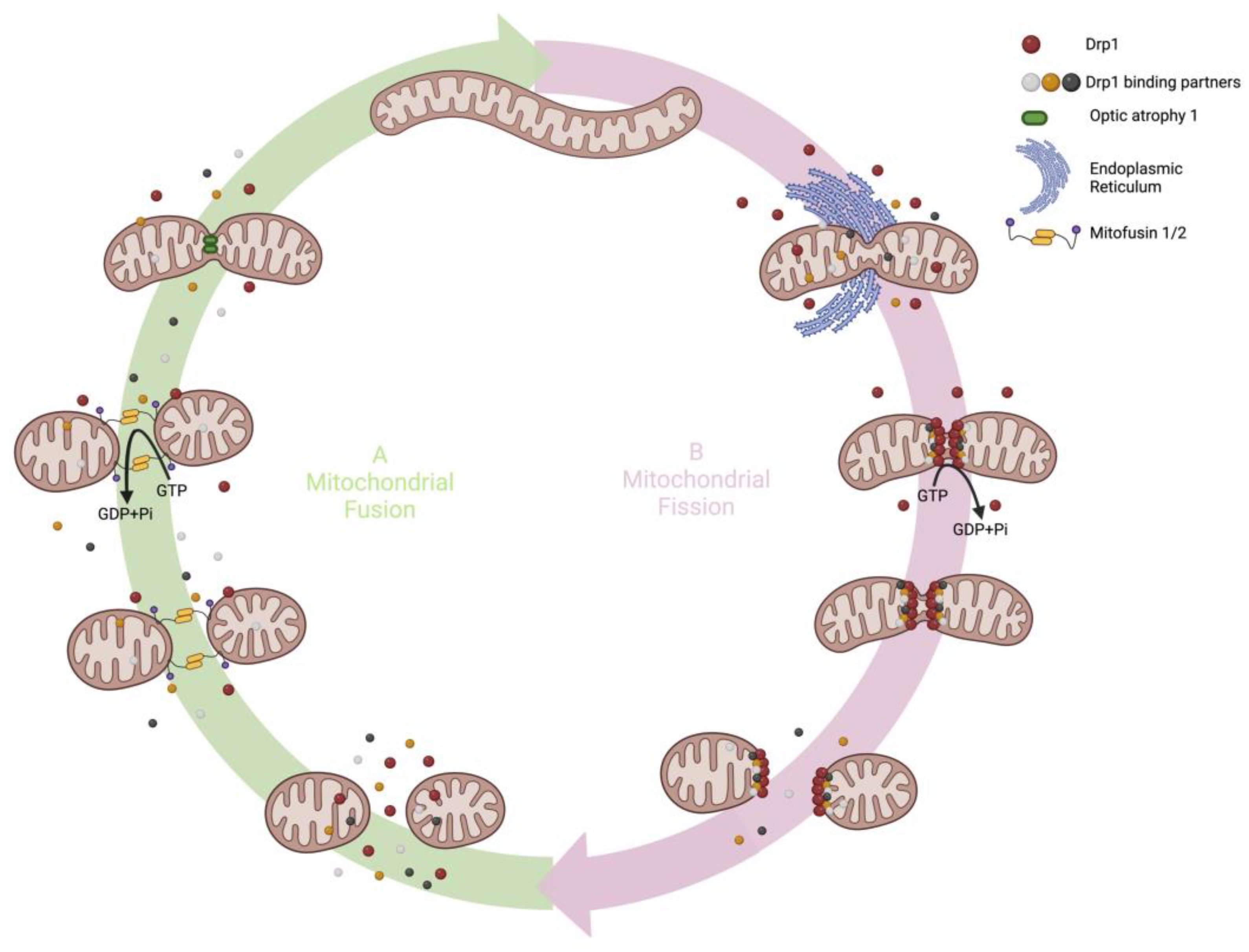
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Do You Have Low Energy? – Upgrade Your Power Supply # EVOO – Blog # 64 – The Virgin Olive Oiler Fermentation is another anaerobic (non-oxygen-requiring) pathway for breaking down glucose, one that’s performed by many types of organisms and cells. In fermentation, the only energy extraction pathway is glycolysis, with one or two extra reactions tacked on at the end. Fermentation and cellular respiration begin the same way, with glycolysis.

Source Image: thevirginoliveoiler.com
Download Image
Cellular Respiration | Definition, Steps & Importance – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com The mitochondrial genome of R. americana contains 97 genes of which 92 can be assigned a function (Lang et al. 1997).The gene set comprises 18 protein-coding genes that have not been found in other mitochondrial genomes, but perhaps more interesting is the fact that it contains all of the 44 protein-coding genes previously identified in one or more other non-plant mitochondrial genomes

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
CIMB | Free Full-Text | Mitochondria Have Made a Long Evolutionary Path from Ancient Bacteria Immigrants within Eukaryotic Cells to Essential Cellular Hosts and Key Players in Human Health and Disease Jul 12, 2023PART 2: AEROBIC RESPIRATION IN YEAST. Optional Activity or Demonstration. This part of the lab investigates aerobic cellular respiration by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, also referred to as “baker’s yeast” and “brewer’s yeast.”Yeast is a unicellular fungus that can convert glucose into carbon dioxide and ATP when oxygen is present.
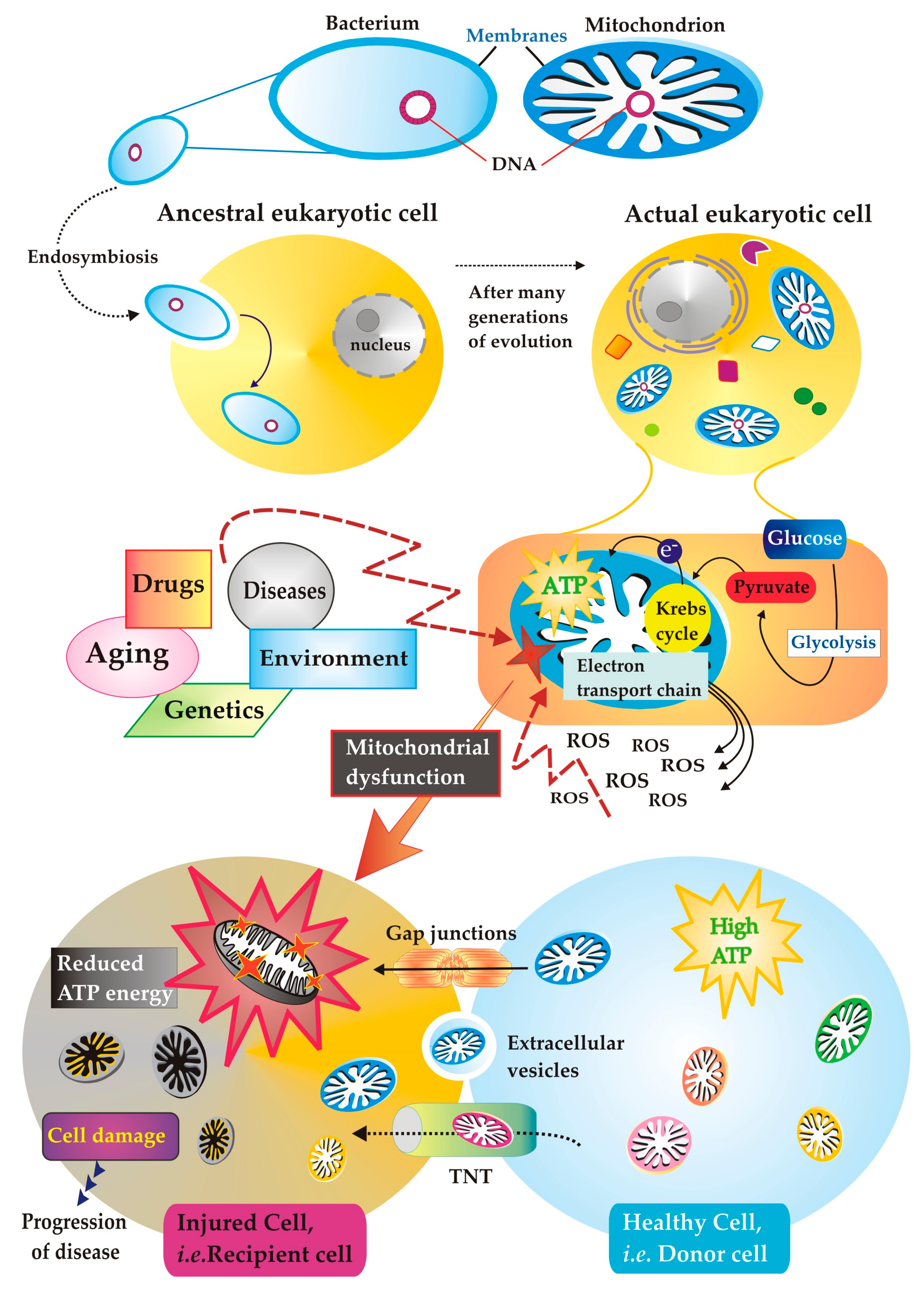
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Peroxisomes and Mitochondria | Biology | JoVE Mitochondria perform numerous biological tasks ranging from bioenergetics to production of protein co-factors, including heme and iron-sulfur clusters. Due to the importance of mitochondria in many cellular processes, mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in a wide variety of human disorders.

Source Image: jove.com
Download Image
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Supercomplexes: From Structure to Function 1. Introduction Mitochondria of eukaryotic cells are surrounded by two biological membranes. The outer membrane that separates mitochondria from the cytosol is permeable for solutes due to the presence of voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC).

Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Cells | Free Full-Text | The Role of Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitotic Fission in Regulating the Cell Cycle in Cancer and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Implications for Dynamin-Related Protein 1 and Mitofusin2 in
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Supercomplexes: From Structure to Function 8 Chapter 8 Respiration Respiration by Yeast BACKGROUND. During respiration, yeast undergo metabolic processes to obtain energy from the breakdown of sugars. However, yeast can only metabolize certain types of sugars. In order for yeast to utilize a particular sugar as a food source, it needs to have specific transport mechanisms to bring the sugar molecules into its cells.
Cellular Respiration | Definition, Steps & Importance – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Peroxisomes and Mitochondria | Biology | JoVE Jul 12, 2023PART 2: AEROBIC RESPIRATION IN YEAST. Optional Activity or Demonstration. This part of the lab investigates aerobic cellular respiration by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, also referred to as “baker’s yeast” and “brewer’s yeast.”Yeast is a unicellular fungus that can convert glucose into carbon dioxide and ATP when oxygen is present.