Problem solved. (If you ignore the fact that you’re still locked inside your office!) The mechanics of transcription In cells, transcription is the process that resembles copying a recipe onto a 3×5 card and sliding it under the office door.
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until a. the two … | Channels for Pearson+
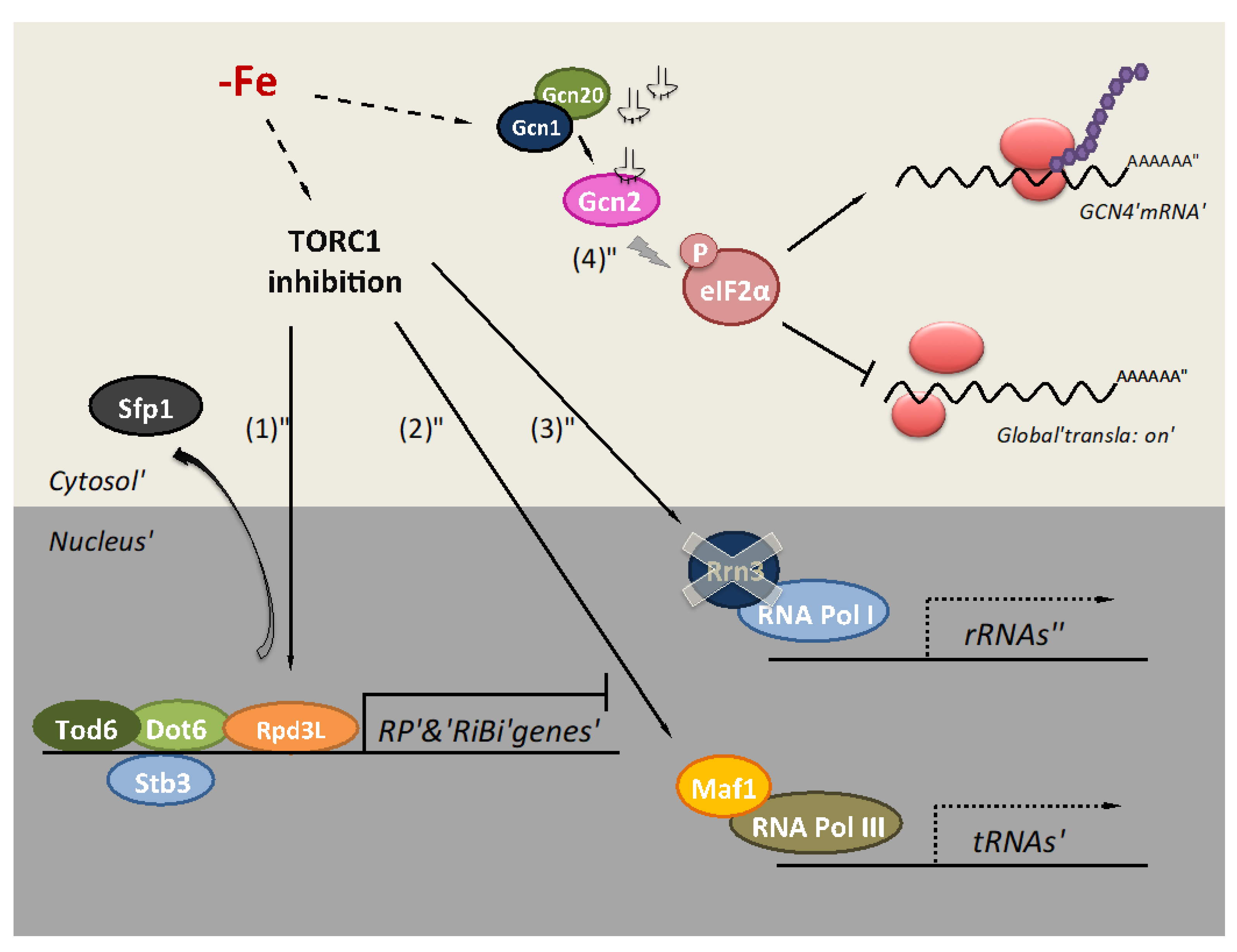
Eukaryotic transcription is a tightly regulated process that requires a variety of proteins to interact with each other and with the DNA strand. Although the process of transcription in eukaryotes involves a greater metabolic investment than in prokaryotes, it ensures that the cell transcribes precisely the pre-mRNAs that it needs for protein
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
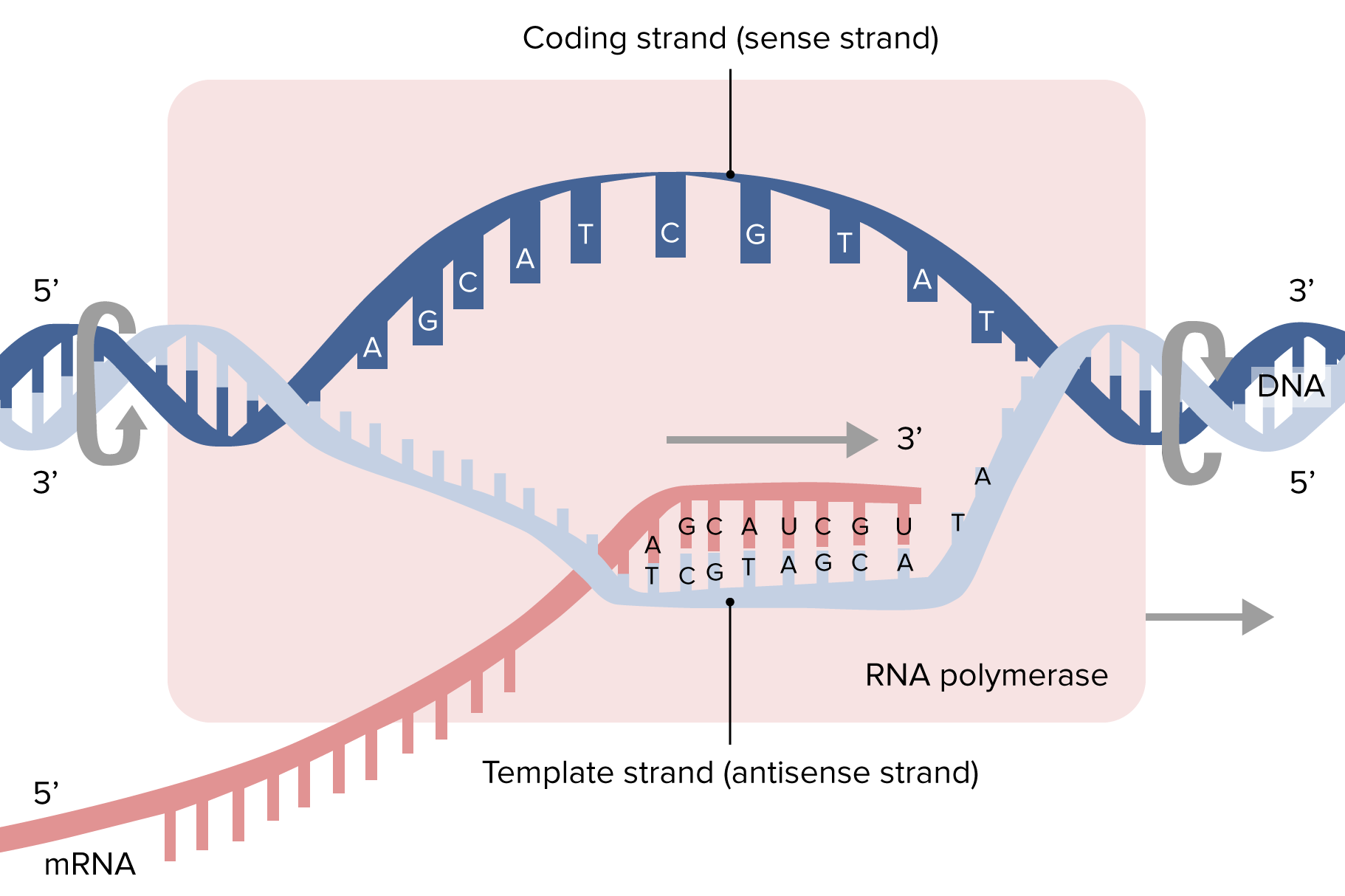
As in bacteria, transcription in eukaryotic cells is controlled by proteins that bind to specific regulatory sequences and modulate the activity of RNA polymerase.
Source Image: lecturio.com
Download Image
DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase Mediates YB-1 (Y-Box Binding Protein)-Induced Double Strand Break Repair | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
This page titled 3.5.4: Eukaryotic Transcription is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by OpenStax via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes perform fundamentally the same process

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
In Eukaryotic Cells Transcription Cannot Begin Until
This page titled 3.5.4: Eukaryotic Transcription is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by OpenStax via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes perform fundamentally the same process
Like prokaryotic cells, the transcription of genes in eukaryotes requires the action of an RNA polymerase to bind to a DNA sequence upstream of a gene in order to initiate transcription. However, unlike prokaryotic cells, the eukaryotic RNA polymerase requires other proteins, or transcription factors, to facilitate transcription initiation.
De Novo Designed Protein-Interaction Modules for In-Cell Applications | ACS Synthetic Biology
Question 1 Textbook Question In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until a. the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter. b. several transcription factors have bound to the promoter. c. the 5′ caps are removed from the mRNA. d. the DNA introns are removed from the template. practice Privacy and cookies
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until | Filo

Source Image: askfilo.com
Download Image
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until a. the two … | Channels for Pearson+
Question 1 Textbook Question In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until a. the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter. b. several transcription factors have bound to the promoter. c. the 5′ caps are removed from the mRNA. d. the DNA introns are removed from the template. practice Privacy and cookies

Source Image: pearson.com
Download Image
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until a. the two … | Channels for Pearson+
As in bacteria, transcription in eukaryotic cells is controlled by proteins that bind to specific regulatory sequences and modulate the activity of RNA polymerase.

Source Image: pearson.com
Download Image
DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase Mediates YB-1 (Y-Box Binding Protein)-Induced Double Strand Break Repair | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
Problem solved. (If you ignore the fact that you’re still locked inside your office!) The mechanics of transcription In cells, transcription is the process that resembles copying a recipe onto a 3×5 card and sliding it under the office door.

Source Image: ahajournals.org
Download Image
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until a. the two … | Channels for Pearson+
Dec 30, 2022Figure 8.3.5 8.3. 5. Eukaryotic Transcription. An initiation complex of several transcription factors is needed to dock the RNA Polymerase II in position to begin transcription. This binding of the promoter by TFIID occurs independently of RNA Polymerase II, and in fact, RNAP II will not attach to TFIID at this time.

Source Image: pearson.com
Download Image
Beyond Transcription: Roles of Transcription Factors in Pre-mRNA Splicing | Chemical Reviews
This page titled 3.5.4: Eukaryotic Transcription is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by OpenStax via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes perform fundamentally the same process

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
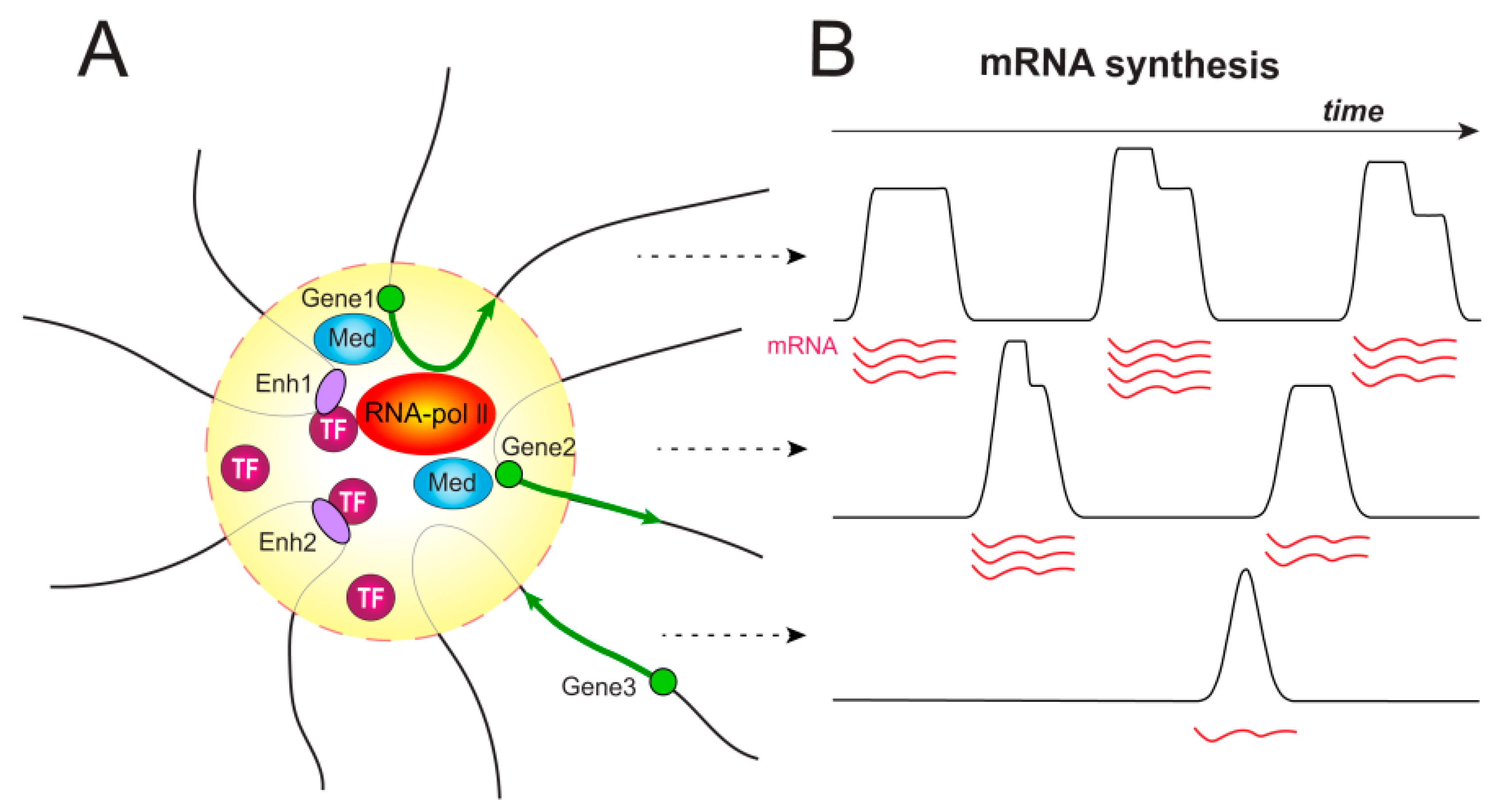
Cells | Free Full-Text | Molecular Basis of the Function of Transcriptional Enhancers
Like prokaryotic cells, the transcription of genes in eukaryotes requires the action of an RNA polymerase to bind to a DNA sequence upstream of a gene in order to initiate transcription. However, unlike prokaryotic cells, the eukaryotic RNA polymerase requires other proteins, or transcription factors, to facilitate transcription initiation.
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until a. the two … | Channels for Pearson+
Cells | Free Full-Text | Molecular Basis of the Function of Transcriptional Enhancers
Eukaryotic transcription is a tightly regulated process that requires a variety of proteins to interact with each other and with the DNA strand. Although the process of transcription in eukaryotes involves a greater metabolic investment than in prokaryotes, it ensures that the cell transcribes precisely the pre-mRNAs that it needs for protein
DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase Mediates YB-1 (Y-Box Binding Protein)-Induced Double Strand Break Repair | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology Beyond Transcription: Roles of Transcription Factors in Pre-mRNA Splicing | Chemical Reviews
Dec 30, 2022Figure 8.3.5 8.3. 5. Eukaryotic Transcription. An initiation complex of several transcription factors is needed to dock the RNA Polymerase II in position to begin transcription. This binding of the promoter by TFIID occurs independently of RNA Polymerase II, and in fact, RNAP II will not attach to TFIID at this time.